08, July 2024
Teaching a chapter, assigning homework, and conducting assignments and exams related to the subjects is the conventional approach. In fact, it is a common structure for facilitating education, but does it benefit all students?
Some students succeed in keeping up with the pace of the class, while others falter due to their inability to understand the teacher’s instruction. Similarly, it is difficult for teachers to monitor student progress or decline individually. That is why Bloom’s taxonomy is the ultimate tool that helps streamline teaching and learning activities.
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s taxonomy is a pedagogical framework that has been divided into three hierarchical models that categorise learning levels. In fact, it has six levels of learning objectives that ascend from the bottom to the top.
From recalling general facts or specific information about a topic or subject to creating something new and original, the taxonomy provides necessary guidance. Besides, educators have used it for many decades to plan lessons and facilitate effective classroom sessions.
Also, it provides an easy mechanism to identify and improve students’ weaknesses through different assignments. For example, when teachers implement assessments, the subsequent results allow them to gauge learners' knowledge levels.
Strategies For Effective Teaching Using Bloom’s Taxonomy
Development of Taxonomy
An educational psychologist named Benjamin Bloom collaborated with his colleagues and developed Bloom’s taxonomy in the 1950s. Furthermore, Mr. Bloom worked with Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl to establish a system of cognitive functioning levels.
They conducted a series of studies on student achievement and educational outcomes and succeeded in determining contributing factors to learning. Also, the taxonomy has undergone a couple of changes throughout the decades, allowing it to update as per educational demands.
Moreover, educators were able to deduce certain crucial findings with the help of the framework, such as:
- Inside and outside the school environment (home, community) equally impact student learning.
- Lack of teaching variation and following a universal curriculum fail to meet students’ learning requirements.
- Students would learn better if teachers employed individualised educational plans.
- Bloom’s Mastery Learning Procedure is instrumental in organising particular concepts and skills into week-long units or study models.
- When students complete each unit, teachers will conduct assessments, helping to ascertain students’ learning.
- The assessments will help to determine the areas where students need additional guidance.
Structure of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Educational psychologists David Krathwol and Lorin Anderson modified Bloom’s taxonomy in 2001 and published a revised version. They published the revised version, titled A Taxonomy for Teaching, Learning, and Assessment.
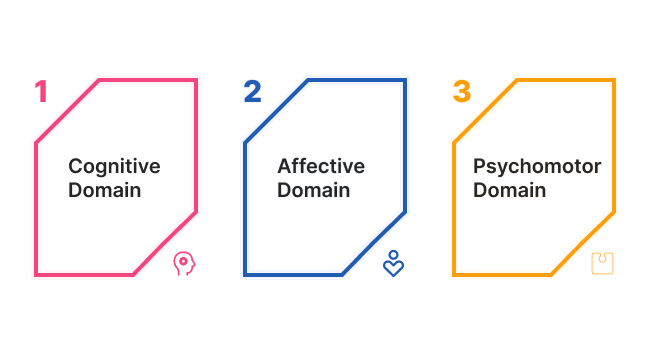
What’s new about the revised taxonomy? The 2001 version shifts away from a fixed educational structure to a dynamic one and integrates the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains.
Cognitive Domain
The cognitive domain deals with intellectual skills, including creative thinking, critical thinking, problem-solving, and creating a knowledge base. Also, it entails starting with simple memorization to create something original based on accumulated knowledge.
Affective Domain
Attitudes, values, interests, and learners’ appreciation are central to the affective domain and are a crucial part of the taxonomy. It starts with receiving and listening to information and continues with characterization and acting upon it.
Psychomotor Domain
Physical development is just as important as cognitive development, and that is why the psychomotor domain is indispensable. Moreover, the psychomotor domain relates to students’ ability to complete physical tasks with movements and skills. For instance, engaging in activities that integrate different sensory perceptions.
Implementing Teaching and Learning with Bloom’s Taxonomy
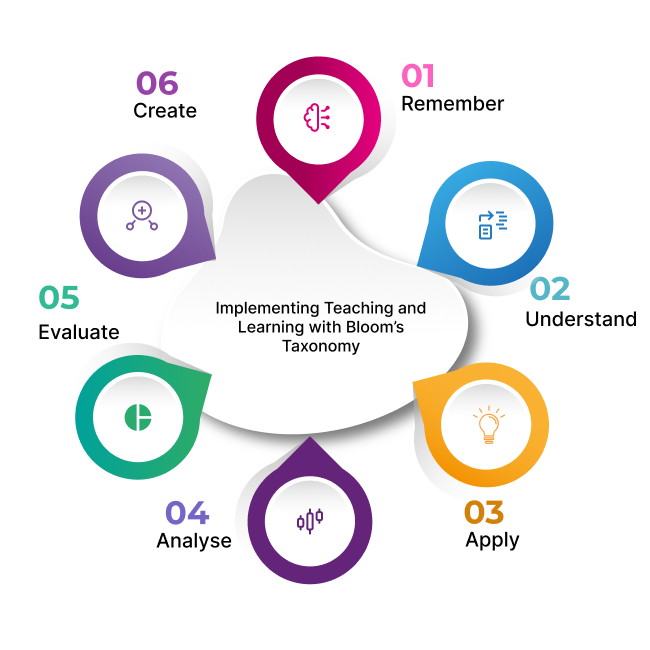
Remember
The hierarchical structure of the taxonomy starts with the lowest level, which is the remembering level, reflecting students’ ability to recall facts. Besides, before starting a lesson, it is useful to check whether students have any prior knowledge.
Therefore, they can conduct a few activities, enabling students to try and recall previously obtained information. For example, teachers can conduct impromptu quizzes or short question-and-answer sessions.
On the other hand, teachers can improve students’ memory skills through the above-mentioned and other exercises. Besides, students succeed in retaining crucial facts and improving long-term memory with unique approaches such as mnemonic devices.
Also, teachers must use the following verbs while creating exercises for remembering: define, describe, identify, label, list, match, name, outline, quote, recall, report, reproduce, retrieve, show, state, tabulate, etc.
Understand
When five out of ten students grasp the concept or lesson faster and learn better,what happens to the other five students? Unfortunately, the last five students, or in most cases, a considerable number of students in a class, fail to express their issues.
It is a common scenario, especially when finishing the lesson and completing the syllabus take precedence over everything else. Hence, teachers can take steps to determine students’ understanding and improve their comprehension abilities.
One of the first steps is adopting a pedagogy that allows teachers to conduct various activities that urge students to provide in-depth explanations. It does not necessarily always have to be essay or long answer writing tasks. On the contrary, group discussions or debates are great for assessing learners’ understanding.
Teachers can use verbs while planning activities: describe, explain, paraphrase, restate, give original examples, summarise, contrast, interpret, discuss, etc.
Pedagogy Vs Andragogy: Difference Between Pedagogy And Andragogy In Learning
Apply
Studying just for the sake of studying does not add value to students’ learning experience or life in the long run. That is why rote memorization does not account for any real advantage beyond passing a test.
However, imagine a situation wherein one needs to solve a problem or demonstrate a skill but can’t because they don’t know how to apply the knowledge. No wonder the taxonomy includes the ‘’application’’ level, which denotes applying what students have learned.
Hence, carrying out experiential learning activities is one of the most significant strategies that teachers can adopt. Whether it is inquiry-based learning or project-based learning activities, both allow students to research, explore, and execute.
Additionally, teachers can assign group projects, motivating them to delve into real-world problems by searching for valid solutions. They can add suitable verbs: calculate, predict, apply, solve, illustrate, use, demonstrate, determine, model, perform, and present.
Analyse
Teaching and improving analytical abilities at the school level is the best way to ensure that children grow to become good thinkers. Furthermore, analytical ability enables individuals to ascertain facts before believing them blindly.
The responsibility of fostering analytical ability rests on teachers, which they can carry out through many exercises. For instance, teachers can conduct the following:
- Conduct debates on opposing topics and list out the merits and demerits of both.
- Encouraging students to create mind maps
- Assigning microlearning exercises to difficult topics.
They can use verbs such as classify, break down, categorise, analyse, diagram, illustrate, criticise, simplify, associate, etc.
Evaluate
How many topics have I covered in math, science, and literature? Which topics and concepts need further explanation? Did I make any progress between the previous and current examinations?
Students must ask themselves such critical questions, helping to self-evaluate their learning and academic progress so far. Teachers will continue to do their bit by monitoring students’ performance and recording their improvement.
However, students can evaluate their learning as well through self-assessment and tracking study habits. Additionally, they can also maintain a journal and note their on-going learning objectives and progress.
Create
Creation is the highest level in Bloom’s taxonomy hierarchy and entails creating something new or original through acquired knowledge. By the time students reach this stage, they become adept at analysing and understanding.
Therefore, teachers must employ adequate challenges and activities that stimulate their thought processes. They can conduct projects that encourage students to work on issues affecting the world, such as global warming.
Likewise, they can develop blueprints for disaster management scenarios that can tackle the aftermath of various events.
Key Takeaways,
Bloom’s taxonomy is one of the most notable pedagogical frameworks that teachers use to track and improve student learning. The six levels of the framework enable teachers to monitor students’ overall improvement in three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor.
Additionally, it allows teachers to align the pedagogy with the learning outcomes and implement suitable teaching and learning activities.
Simplify your faculty hiring process with MasterSoft’s faculty management system.
Mobile: 08448010216
Email: janki.somani@iitms.co.in













