30, August 2021
India is one of the most culturally diverse and prominent countries in the world and has achieved many feats ever since independence. But if we were to talk specifically about the education which forms the future of a nation then there are a lot of things to consider.
There are around 14,94,052 schools in India including Government, Govt Aided and Private Schools.
Despite these numbers, educational practices lacked in terms of “quality” until the introduction of the National Curriculum Framework.
The traditional educational structure was focused on examining the students quarterly or annually. It was mechanical and caused a sense of competitiveness in the children from an early age.
It diminished the interest of students in learning, gave no scope for the growth of creative intelligence as well as did not contribute to personality development.
National Curriculum Framework 2005 was published to guide the institutions and schools to encourage the overall development of the children and to move away from textbook-centric learning.
Let us understand the National Curriculum Framework & its purpose.
What is National Curriculum Framework (NCF 2005)?
A curriculum framework is a standardized format or organized plan or learning outcome that drives the curriculum for courses. It aims to define clear outcomes expected the students to achieve or know in their course.
It is introduced in new educational approaches such as outcome-based education or standards-based education reform design.
A curriculum framework is a set of rules or standards or learning outcomes that states the expectations from students in form of content to be learned. It gives a standard for what they should know and be able to do after completing a course. It is a part of standards based reform design or outcome based education.
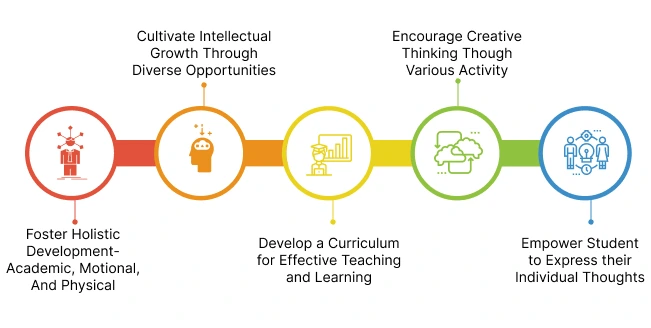
- To promote a wholesome development of the child encompassing the academic, emotional, physical, and emotional aspects
- To enable the students to develop intellectual quotient by providing them varied opportunities
- To make the environment conducive to quality learning where the students would be encouraged to participate in various activities
- To foster creative thinking skills by facilitating different activities and giving the liberty to express individual thoughts within the class
- In response to multi-cultural attributes, the schools must ensure no student is discriminated against based on caste or religion, and social status
Objectives of National Curriculum Framework - NCF 2005
- Introducing the concept of learning without too much load by reducing the syllabus
- All children should have access to quality education without any discrimination
- Curricular practices should be in alignment with secularism, social justice, and equality
- Strengthening a national education system in the society
Important aspects that are covered in NCF 2005 include children’s interest in learning, and feeling valued and heard. The school and curriculum must create a friendly classroom environment and make the students feel safe and appreciated. They must ensure student’s physical, mental, and social growth.
Guiding Principle of National Curriculum Framework - NCF 2005
The NCF 2005 has stated 5 guiding principles for the curriculum development of the students-
- Connecting learning to real-life examples outside school
- Ensuring different learning approaches rather than rote methods
- Enhancing the curriculum to offer knowledge and experiences beyond textbooks
- Improving flexibility of taking examinations and integrating them with class school life
- Enhancing an overriding identity informed by concerns within the democratic polity of the country.
Improve your Institute’s Management along with Teaching- Learning Methods with MasterSoft!
Important Components of National Curriculum Framework (NCF 2005)

The following are the important components of the National Curriculum Framework...
#1: Social Context
Students belonging from disadvantaged sections of the society living in rural areas are especially in vulnerable conditions due to the inadequate educational system. The gender bias running along with the families also is a major problem as it acts as a deterrent for the girls who want to go to school. But they are not able to attain education because their parents believe that educating a girl child is of no real value. After all, ultimately they would be married off.
On the other hand, the increasing commercialization of education has only helped to widen the gap of educational needs. While high-cost private schools can be attended by the children of urban elites, the others who are from working-class families can afford schools with the average and sub-standard curriculum.
Thus the social context of education of India indicates many challenges which should be included in the framework. The National Curriculum Framework for Schools emphasizes that schools must implement pedagogical practices. Such as critical awareness and openness to engage with different communities to share ideas and exchange curricular decisions.
#2: Learning and Knowledge
Learning should be facilitated in such a way that it attracts the attention of the students, rather than confining to the age-old traditional methods of education new approaches should be sought out. An educational ERP software could be introduced for minimizing the hassles in the teaching-learning journey.
#3: The Primacy of the Active Learners
Schools and institutions are the medium through which the students get to know about society, their culture, and the world around them. This formal process of learning is significant because it helps to inculcate knowledge, but the possibilities of understanding and relating to the world are stunted if the methodologies are antiquated and uninspiring.
Child-centered pedagogy should be implemented because it will encourage the children to voice their opinions and experiences through active participation.
Usually, when children respond to a question asked by a teacher they just repeat the answers of the teachers, the curriculum should be designed in such a way that it engages them to find their voices and nurture their curiosity. A school ERP system could be useful to design an impactful curriculum.
#4: Learners in Context
Creating a learning environment that is based on fear, extreme discipline and stress can only lead to inadequate learning. At the same time curriculum, load, and examination-related stress can lead to further problems, all of these should be addressed properly.
Along with academics, physical development should also be a priority, and for that participation in formal, informal play, yoga and other sports-related activities should be encouraged
#5: Development and learning
Keeping in mind that the period from infancy to adulthood is a period of growth and change, hence the National Curriculum Framework for School Education also takes into account the holistic development of the students.
Learning needs to be paced which would allow the students to understand the core concepts as per their understanding. An important aspect to be noted is that the educator should make sure that he or she provides a variety of challenges because passive learning is counter-productive.
#6: Curriculum and Practice
Within the classroom collaborative learning should be facilitated which will provide the opportunity for sharing multiple for interchange of multiple views and opinions. Various pedagogical tools such as school ERP with online assessment system must be implemented for enriched learning experience such as:
- Conducting interactive discussions & quiz sessions where the children can ask questions and then answer those questions depending on what they learned at school and their personal experiences.
- Intelligent guessing should be encouraged as well wherein the student can have the liberty to share his perspective on a matter.
- Active engagement should be encouraged through various classroom activities such as inquiry, exploration, debates, application & reflection
#7: Critical Pedagogy
Teacher and student engagement is important within the classroom as it helps to improve participatory learning. The role of the teacher is to create a safe and inclusive environment for the students to express themselves freely without having to worry about being judged.
It is noteworthy to mention that when teachers and students share and reflect on their individual experiences it helps to learn about varied social realities.
Difference Between Pedagogy And Andragogy In Learning
Curricular Area, School Stages, and Assessment
The major areas concerning curricular planning have been the same; it is important to reevaluate these areas elaborately and verify if the new alterations and additions are aligned in context with the emerging social needs.
1.Language
The National Curriculum Framework for Schools emphasizes the fact that language teaching should be multilingual wherein the students should be taught in a three-language structure.
The mother tongue should be prioritized as the first language, in Hindi-speaking states the third language ought to be modern English; in non-Hindi-speaking states, Hindi should be taught since it is the national language.
2.Mathematics
The higher goal of mathematics education is to help the child think and reason mathematically, to make assumptions based on logical reasoning. The primary goal is to:
- Help the children understand the core mathematical concepts of algebra arithmetic, geometry, and trigonometry.
- To provide them the idea as to how the mathematical concepts lead to structuration, generalization, and abstraction.
- Oftentimes mathematics is thought to be difficult and hard to understand, but with the help of varied representations, mathematical concepts can be taught easily.
3.Computers
The advancement of modern technology has urged institutes and schools alike to give attention to educating the students about the usage of computers. But it is important to note that schools lack the infrastructural resources to provide adequate knowledge regarding this.
Hence the school body or authority should make it a point to look for viable and innovative alternatives in case of lack of required funds. Connectivity and software technologies are available which are appropriate for schools in rural and urban schools.
4.Science
Science plays a significant role in educating children wherein they can differentiate between facts and fiction; the Pedagogy should be prepared in such a way that it incorporates activities, observations, and experimentation.
Instead of information-based learning, the educators should encourage an active approach towards science and how he or she connects it with the world around them.
5.Social Sciences
Subjects such as history, geography, political science, economics, sociology, and anthropology are significant as it helps to educate the child about his or her social reality. Multi-disciplinary approaches should be indicated as this collectively helps to instill a strong sense of human values such as trust, mutual respect, freedom, and respect for diversity.
6.Art Education
Arts has never been given any importance and is often confined to either “useful hobbies or leisure activities’’ and they are only used as a tool to showcase the grandiosity of the school during scholastic events. No longer should the arts be ignored, on the contrary, they should work towards nurturing the artistic capabilities within the children.
7.Health and Physical Education
Undernourishment and communicable diseases are a few of the most vital health issues that cause children to suffer in India. Keeping in mind this aspect the school authorities should make sure that vulnerable social groups and girl children are attended to and taken care of properly. This subject aims to provide an understanding of the overall importance of health and physical fitness.
8.Work Education
Work education is related to incorporating activities that would ultimately help the students inculcate necessary life skills like problem-solving, creative thinking, situation-based analysis, and effective communication.
The institutes should provide enough opportunities in terms of pedagogical strategies to help the students develop these skills from an early age.
9.Education For Peace
The world is constantly amidst violence, chaos, and dispute, despite these unpleasant realities the responsibility of the school is to ensure imparting of value-based education.
Schools must ensure that there is no indication of violence in their teachings. It is important to incorporate tolerance, justice, intercultural understanding, and civic responsibility within the educational structure.
NCF 2020 (National Curriculum Framework - 2020) - A Complete Guide
How MasterSoft Can Help Schools to Take Care of the Learning Needs of Students?
MasterSoft, being the leading edTech provider, understands the reforms suggested by the National Curriculum Framework. To successfully meet the systemic reforms in areas of teaching, curriculum, strategies to be implemented, MasterSoft team offers a School ERP Software integrated with Learning Management System (LMS). Below mentioned are a few of the highlights of the school ERP software:
- E-learning Modules:- E-learning modules of the school ERP enable teachers to develop a learner-centric curriculum that would take care of the learning needs of the students.
- Skills Development:- Taking a cue from the 2005 NCF the reforms suggested in National Curriculum Framework 2020 is to emphasize activities that would promote critical thinking along with that making learning more inquiry-based,discovery-based, discussion-based, and analytical. The LMS system is based on the framework of Bloom’s Taxonomy and promotes the same.
- Integrated System:- Opting for an integrated model for teacher education wherein educators would be inculcated with counseling skills.
FAQ's On National Curriculum Framework - (NCF 2005)
A curriculum framework is a well organized plan or standards that defines what students must know and be able to do in terms of clear, definable standards. A curriculum framework is part of an outcome-based education reform design.
The National Curriculum framework 2005 (NCF 2005) is the set of guidelines for textbooks, syllabus, teaching practices, for schools in India. It was published in 2005 by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) in India.
- School and class environment reforms
- Learning and knowledge process reforms
- Perspective reforms
- Curriculum and assessment reforms
- Systemic reforms
- High emphasis on marks and grade system
- Huge burden on the teachers
- Rote based learning approach of students
- Students do not understand what they are learning
- Lack of supervisory staff in institutes
The Fastest, Easiest, and Most Reliable Educational ERP System to Meet the Needs of Your School
Mobile: 08448010216
Email: janki.somani@iitms.co.in













