Updated On 27, Feb 2025
Most higher educational institutes strive to attain a position amongst the top colleges or universities of the country. Methodologies such as the NIRF ranking and accreditation are standardised methods that enable institutes to enhance their reputation and increase enrolment.
Although both methods contribute to the institute’s improvement and evaluation, they have core differences in terms of operation, criteria, and purpose. Hence, let’s take a look at the difference between NIRF ranking and accreditation.
Accreditation vs. Ranking
Accreditation and ranking are primary mediums through which the Ministry of Education, Government of India, and accrediting agencies regulate the country’s education system. Both authoritative bodies establish a set of standards, according to which institutes carry out action plans to improve the teaching and learning processes.
Furthermore, institutional support, student performance, faculty performance, governance, graduate outcomes, inclusivity, etc., are key focus areas. However, crucial differences persist in terms of methodologies, metrics implemented to prepare reports, etc.
Accreditation
Accreditation is a formal process of institutional evaluation wherein the government-approved accrediting agency measures the quality of a program or college/university. The initial accreditation cycle typically lasts for 5 years, after which a periodic review process is conducted to ensure that the institute complies with quality standards.
Besides, the NAAC accreditation process is rigorous, and only a handful of institutes across India have succeeded, signifying the high standards set by the accreditation body.
Ranking
The NIRF ranking is an annual event that takes place every year, wherein the Ministry of Education, Government of India, releases a list. The list contains a number of higher education institutes that are ranked according to different categories.
Let us discover more about the NIRF Rankings:
What is the NIRF Ranking?
NIRF stands for National Institutional Ranking Framework, which is an innovative strategy that the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) approved and launched in September 2015. It provides a mechanism to rank higher educational institutes based on a pre-established set of criteria.
The primary objectives of NIRF rankings are to enhance the overall quality of higher education and acknowledge institutes that excel in various areas. The ranking mechanism also provides valuable insights to stakeholders, including students, researchers, parents, policymakers, and industry.
Most importantly, it ensures that institutes function effectively to meet their goals and improve academic and non-academic activities. The different categories of institutes eligible for the NIRF rankings are as follows: architecture, engineering, pharmacy, management, law, medical, dental, research institute, college, university, and others.
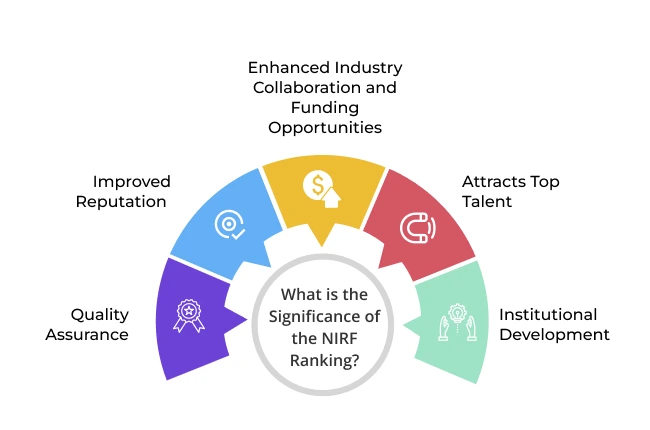
What is the significance of the NIRF ranking?
Quality Assurance:
A high NIRF ranking suggests that the institute has implemented the necessary policies and changes, ensuring excellent academic quality and infrastructure, qualified faculty, etc.
Improved Reputation:
A high rank improves an institute’s reputation through enhanced credibility, increasing national and international recognition.
Enhanced Industry Collaboration and Funding Opportunities:
Institutes succeed at collaborating with prominent industries and experts, resulting in internships, research projects, job placements, etc. Simultaneously, they have higher chances of securing funds and research grants from private organisations and government agencies.
Attracts Top Talent:
Talented and brightest students prioritise top-ranking institutes as they want to receive quality education.
Institutional Development:
A high ranking serves to motivate higher educational institutes to improve in the core areas such as student support services, teaching, infrastructure, research, etc.
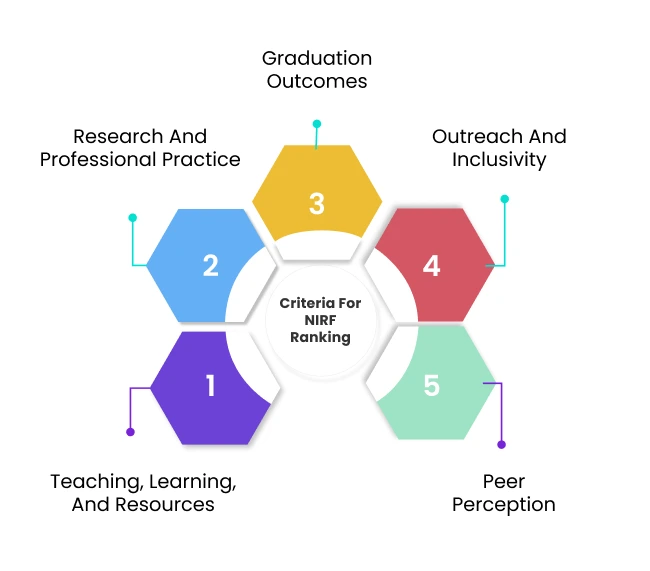
Besides, the ranking takes place based on institutes’ performance on five parameters/criteria, which are as follows:
- Teaching, learning, and resources
- Research and professional practice
- Graduation outcomes
- Outreach and inclusivity
- Peer perception
Criteria for NIRF Ranking
The parameters or criteria allow the Ministry to carry out a comprehensive assessment of the institution’s performance. The criteria are as follows:
Teaching, Learning, and Resources
The first criteria of the National Institutional Ranking Framework is Teaching, Learning, and Resources (TLR), which highlights an institute’s educational activities. It measures the number of teachers, the quality of instructional processes and approaches, resources for research work, and additional academic facilities.
Therefore, LTR is instrumental in evaluating academic and non-academic resources that the institutes provide for students’s overall development.
Research and Professional Practice
Faculty/teachers are primary stakeholders who are responsible for students’ learning and growth; hence, their contribution to research activities is of paramount importance.
Also, it focuses on the number and quality of research projects, the number of published research papers, filed and granted patents, etc. This parameter assesses to what extent an institute generates new knowledge and contributes to global academic knowledge.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF): A Comprehensive Overview
Graduation Outcomes
Graduation Outcomes (GO) measures the rate of successful graduates per class in a year and students’ overall career progression. It sheds light on the programs and courses’ effectiveness in terms of making students employment-ready or industry-ready. In effect, the parameter motivates institutes to shift from rote learning to output-based instructional activities.
Outreach and Inclusivity
Outreach and Inclusivity (OI) evaluates an institute's initiatives to facilitate equitable educational opportunities for all students regardless of gender, caste, and religion. It accounts for student diversity: the percentage of students from different states, marginalised social groups, female students, etc. Additionally, it highlights an educational institution’s social responsibility through outreach programs and community engagement.
Peer Perception
A strong peer perception influences an institute’s reputation, helping to attract talented faculty and students and increase industry collaborations. Therefore, peer perception is the last yet one of the crucial parameters indicating the institute's reputation among other institutions, academic peers, faculty members, industry experts, etc.
How does the NIRF collect data and what are its procedures?
The NIRF has a defined process of collecting data and ranking higher education institutions. This is how it is done:
How does the NIRF collect data and what are its procedures?
- Data Collection: The data collection process is held annually. It is done through a dedicated online portal. Institutions must thus submit their data within the allotted period if they wish to take part in the ranking process.
- Ranking Parameters: Teaching, learning, and resources (TLR), research and professional practice (RP), graduation outcomes (GO), outreach and inclusion (OI), and perception (PR) are the five criteria used to rank.
- Data Verification: After the institutions submit the data, it goes through a number of checks, including validation by the NIRF. It is done either by self-declaration of institutes, third-party verification, or random checks.
- Scoring and Ranking: Based on the pre-defined metrics, the institutions are scored and ranked. The final scores are decided in their respective categories like universities, engineering colleges, and so on.
- Ranking Publication: The Ministry of Education publishes the final ranks on the NIRF website and announces it publicly.
- Feedbacks: In case the institutions find the rankings irrelevant from the data provided, they are free to give feedback and make an appeal.
- Continuous Improvement: The NIRF classification, like any other accreditation, is determined by an annual review that emphasizes excellence and continuous improvement.
What are the challenges and future scope of NIRF?
Let us discuss the challenges and the opportunities the National Institutional Ranking Framework holds for the future.
-
Problem: Lack of Awareness
- Solution: Developing IPR policies and allocating a dedicated budget for the same. Furthermore, conducting regular IPR training workshops might help.
-
Problem: Resource Crunch
- Solution: Pursuing industry-academia partnerships can bring in valuable resources. Dedicating a budget for the same may add up to the ease.
-
Problem: Policy Challenges
- Solution: Implement systems for managing licensing patents.
-
Problem: Limited Collaboration with Industries
- Solution: Rewarding people for patent filing and commercialization.
Strategies for Institutions to Improve NIRF Ranking
Improving the NIRF requires a strategic approach. Here are some of the ways by which the institutions can achieve it.
- Academic Excellence: Design the curriculum as per the industrial trends and demands. Also, motivate the students and faculty members to publish high-quality research papers.
- Infrastructural Improvements: When it comes to advancement, infrastructure development is crucial. Purchasing top-notch technology and renovating classrooms could be quite beneficial.
- Student-Centric Approach: Adopting a student-centric approach is crucial for raising the caliber of NIRF rating. This can be accomplished by using creative teaching methods to increase student involvement.
- Faculty Training: The educational institution must make an investment to enhance the faculty's skill sets. Regular training sessions and workshops can help achieve this.
- Partnership with Industries: In order to get internships, placements, and employment prospects for students, it is now crucial for educational institutions to work with industry. This also improves the NIRF ranking for them.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: The NIRF ranking of the universities is raised by supporting innovations and fresh concepts for start-ups through funding and other means.
- Adopting Sustainability: Integrating environmentally sustainable techniques contributes to the institute's positive reputation.
- Accreditation: Institutions are guaranteed quality by upholding accreditation and other requirements.
- Stakeholders Involvement: The process of improvement is continuous. Therefore, getting input from the stakeholders on a regular basis can aid in raising the standard of instruction.
- Transparency: Improving NIRF ranking is more likely when reliable data is provided to the NIRF portal.
The NIRF ranking follows a weighted scoring system, wherein all five parameters are assigned a specific weight. For example, if an institute gets 60, 50, 70, 90, and 80 marks respectively in the parameters, these marks will be multiplied by the assigned weightage. Likewise, all the other parameters will be calculated in the same way.
The last step is to add all the calculated scores, which provides the aggregate score out of 100, based on which NIRF determines and publishes the ranking. However, it is notable to mention that the weightage for the additional categories, including colleges and architecture, is different. Also, institutes must adhere to the following data capture format:
- Institute/University needs to be filled up by the institution for the past 3 years on NIRF.
- Sanctioned and approved intake
- Total Student Strength
- Placement and Higher Studies (Details need to be provided in Excel)
- Financial Resources
- Sponsored Research Projects (details need to be provided in Excel)
- Consultancy Projects
- Patent (Published and Granted) (Verified from Derwent Innovation)
- Teachers: Awards of National and International Repute
- NBA Accreditation Information of Programs
- Faculty Details
- Publications in SCOPUS and Web of Science will be considered.
Learning Management System - A Comprehensive Guide On LMS Software
How to Improve NIRF Ranking?
Institutes must prioritise the following best practices and methods to improve the NIRF rankings:
Pedagogical Methodologies
Innovative teaching and learning techniques beyond the conventional teacher-centric methods are key to enhancing the education system. Therefore, institutes must encourage the implementation of student-centric learning approaches, experiential learning activities, problem-based learning exercises, etc.
Furthermore, incorporating technological tools like the LMS facilitateseasy access to varied learning resources and materials. In effect, teachers can conduct various pedagogical methods, depending on the learning requirements, and track students’s continuous progress.
Transparency in Admissions
A disorganised and conspicuous admission process often has negative consequences, leading to students’ or parents’ disappointment. Therefore, regulating transparency at every step of the enrolment procedure helps establish and maintain trust between the institute and students.
Some of the crucial steps include providing an updated website featuring all necessary information and ensuring a merit-based selection of applicants. Utilise a robust online admission system, enabling students to complete the procedure while keeping track of their application and admission process.
The institute must provide a transparent fee structure by disclosing all fees upfront so that students don’t have any confusion later.
Varied Courses
Offering multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary courses distinguishes the particular institute from others and attracts students who seek specialised and innovative programs. Besides, it aligns with the NEP 2020 vision that emphasises multidisciplinary education.
Therefore, institutes must include varied courses and foster collaborations with industry representatives, facilitating diverse research projects.
Student Support Services
Institutes investing in infrastructure, faculty, and research and development activities would have little to no outcome if they didn’t fulfil students’ requirements, leading to student dissatisfaction. Comprehensive student support services, including counselling, health services, and career guidance, can make a considerable difference.
At the same time, extracurricular activities and workshops for personality development and a supportive campus environment contribute to high retention rates.
Full-Time or Part-Time Vocational Courses
Possessing additional relevant skills apart from the ones that the students gain from their undergraduate or postgraduate degrees proves to be a notable advantage. Institutes can offer full-time or part-time vocational courses, helping to prepare students with specialised skills.
Consequently, employers and organisations will hire graduates with relevant competencies, ultimately boosting the institute’s placement record.
Collaborations with Industry, Research Organisations, Institutes of Eminence
An educational institute flourishes by expanding its network so it can collaborate with other institutes for joint research projects. They can sign MOUs with industries and organisations for strategic partnerships, student and faculty exchange, research internships, program funding, etc.
2 Week, 4 Week, or 6 Month Technical and Social Internship
Institutes facilitating technical internships indicate their commitment to providing students with opportunities to learn additional skills and knowledge. On the other hand, social services allow students to engage in volunteer and community programs. Therefore, institutes can help students improve their socio-emotional skills, teamwork, and leadership.
Providing social and technical internships can improve NIRF rankings by enhancing students’ employability and promoting social responsibility and community engagement.
Technical and Social Internships
Institutes facilitating technical internships indicate their commitment to providing students with opportunities to learn additional skills and knowledge. On the other hand, social services allow students to engage in volunteer and community programs. Providing social and technical internships can improve NIRF rankings by enhancing students’ employability and promoting social responsibility and community engagement.
Qualified Staff and Balanced Male-Female Ratio
Attaining academic goals directly links with high NIRF rankings, which is difficult to achieve without competent staff. Hence, recruiting teachers with high qualifications (PhD) is an important criterion that institutes must fulfil. Simultaneously, the faculty and staff must establish an enriching teaching and learning environment.
It is equally crucial for institutes to maintain a balanced male-female ratio of students, faculty, and staff (for co-educational institutes only).
Application for Research Funds
Research and development activities are one of the primary parameters for the rankings; therefore, institutes should apply for various research funds. This action plan empowers students and faculty to continue their research projects.
One of the best ways to attract potential sponsors or industry partners is by participating in educational conventions and expos. Such academic events provide an opportunity for institute representatives to explain their ongoing and upcoming research projects in the pipeline.
Patent and Transfer of Technology
Plagiarism or theft is a prevalent issue that compromises the ownership or patent of research or inventions. The research team, including the students and faculty, must patent their research to avoid intellectual property theft.
At the same time, institutes must focus on the transfer of technology, including research data, research materials, and inventions. However, institutes and researchers must abide by the specific laws and regulations.
Pre-placement and Post-placement Assistance
An institute’s responsibility does not end with students’ successful graduation; it continues with placement activities. Implementing output-based education is the stepping stone, allowing students to learn in-demand skills and knowledge. The secondary step is conducting pre-placement activities, including skill development courses/sessions, aptitude tests, and mock interviews.
Finally, the institute conducts job fairs and placement camps, inviting top companies whose representatives can hire graduates who fit the job requirements. Additionally, they provide additional career advice to students dissatisfied with their current jobs and help them with further employment opportunities.
FAQ’s On National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF Ranking)
NIRF, or National Institutional Ranking Framework, is a ranking mechanism that the Ministry of Education, Government of India, adopts to rank higher educational institutes.
NIRF ranking is a quality assurance indicator that reflects an institute’s achievements, credibility and reputation, enhanced student enrolment, etc.
The parameters of the NIRF ranking are as follows:
- Teaching-learning and resources
- Graduation outcomes
- Research, Professional Practice & Collaborative Performance
- Outreach and inclusivity
- Peer perception















