Updated On 20, Feb 2025
Mechanical or rote learning is an outcome of an ineffective or substandard education system, which lingers on a one-size-fits-all approach. Teacher-centric methods are central aspects of the teaching and learning process, providing a limited scope for creative and analytical thinking.
In sharp contrast, experiential learning provides a medium for students to engage actively in problem-solving and independent decision-making. They get the chance to connect the learning material to real-world applications, collaborate, and reflect.
But what is experiential learning, and how does it enrich students’ experiences?
What is Experiential Learning?
Experiential learning is an educational strategy that necessitates a hands-on approach to learning, allowing students to learn directly. It goes beyond the traditional methods of lectures and passive information absorption and urges students to participate, research, and conclude.
Teachers can implement the strategy across different subjects and include activities such as internships, project-based learning, simulations, fieldwork, etc. In effect, students are able to understand core concepts deeply and retain information effectively.
What’s more, teachers can include different techniques, helping to accommodate different learning styles (visual, auditory, and kinaesthetic). For instance, students can rely on video explainers, podcasts, published articles, research papers, etc. Institutes can collaborate with organisations and institutions to facilitate research work, internships, apprenticeship programs, etc.
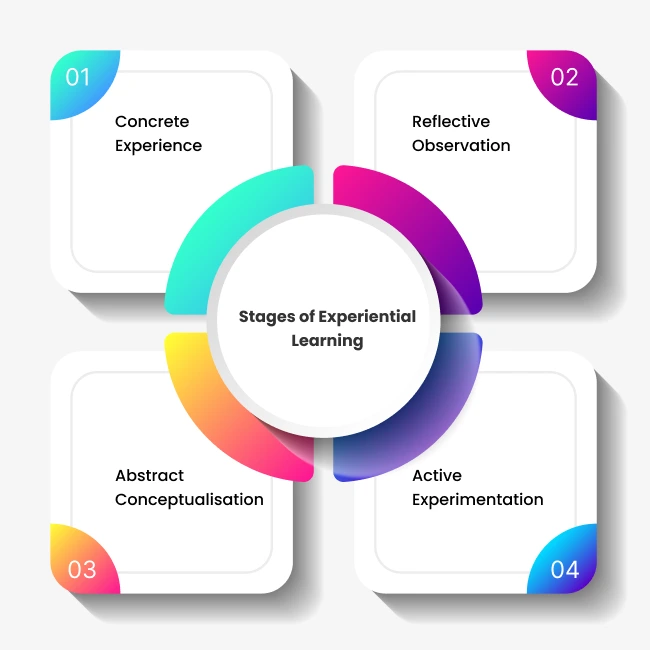
Stages of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is an age-old concept that David Kolb explored in the Experiential Learning Theory (ELT), which lays out a four-stage cycle of how people attain knowledge. The stages of experiential learning are as follows:
Concrete Experience
Concrete experience is the first stage, wherein an individual learns something after undergoing something such as an experiment, simulation, etc. This is when he/she gets to experience directly rather than passively observing. For example, a student works on a project based on a blueprint that he/she has made.
Reflective Observation
Reflective observation relates to reflecting on what they have learnt; they analyse the situation, the action, the result, and the positive and negative outcomes. Learners gain insights by observing a scenario from different perspectives.
Abstract Conceptualisation
The next step after reflective observation is identifying core patterns and principles and taking decisive steps towards making sense of their experiences. For instance, they take extra help from lectures, books, or instructors to gather additional knowledge.
Active Experimentation
The final stage of the learning cycle calls for applying what they have learnt to situations; they carry out their ideas into action. In case they encounter difficulty or unfavourable results, they adapt their strategy accordingly to improve for the next time.
What Is CCE: Importance Of Continuous And Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE)
Tips for Effective Implementation of Experiential Learning
First Step
The initial step before implementing any pedagogical strategy in the classroom is determining the student’s prior knowledge and preparedness. Therefore, teachers must evaluate students’ understanding levels through pop quizzes related to the topic. Also, they need to include socio-culturally appropriate instructional activities.
Second Step
The second step includes planning and scheduling in-class activities that must be aligned with the learning objectives. Simultaneously, the activities must cater to varying learning styles and should encourage students to ask questions and research independently.
Third Step
Teachers must play the role of a facilitator or mediator rather than a lecturer; this will allow students to take ownership of their learning process. Students must reflect on their findings at the end of each experiential learning activity, such as role-playing or fieldwork.
Furthermore, teachers must provide constructive feedback on students’ tasks, enabling learners to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
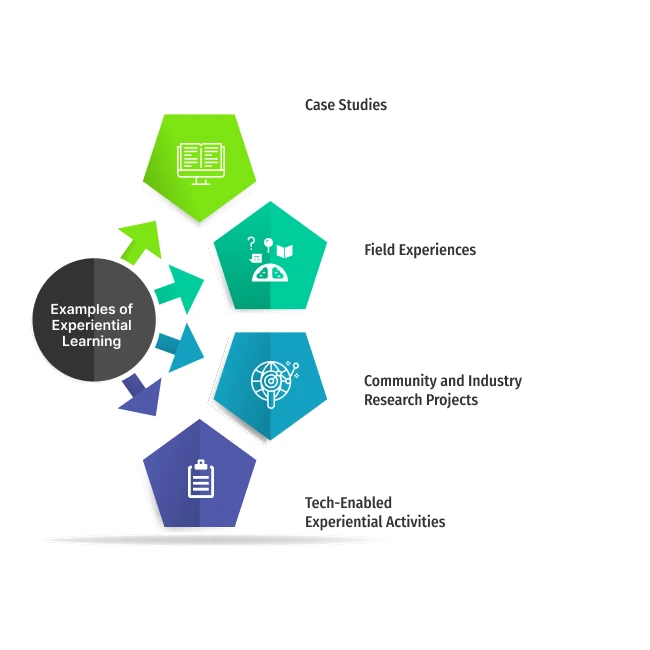
Examples of Experiential Learning
Case Studies
Case studies are excellent experiential learning activities that allow students to work on actual or hypothetical issues. They research and analyse various theories and concepts and make well-informed conclusions.
Case studies can occur independently or in a group, providing an opportunity to include various perspectives. For example, a group of students can investigate the latest aviation disaster, determine its causes, and develop potential mitigation strategies.
Field Experiences
Taking learning beyond the four walls of the classroom is a vital step in the process of stimulating students’ deep thinking abilities. That is where fieldwork can prove to be immensely useful, as it allows students to engage with people, communities, and ecosystems.
Students take part in tasks and surveys, collect data, and note down their observations. Therefore, Kolb’s first and second stages of experiential learning occur when students experience and observe accordingly. Some examples of field experiences are as follows:
- Institutes can collaborate with architecture firms, and students can visit their ongoing projects to understand the nuances of urban infrastructure and how they adhere to policies.
- Students can develop a business plan for launching a start-up and conduct the prerequisites such as financial planning, market research, etc.
Community and Industry Research Projects
One of the best ways to bridge the gap between theoretical learning and practical application is through community and industry research projects. Students get the chance to collaborate with local organisations or community businesses.
For example, internships enable students to get hands-on experience in a particular field, wherein they get to work with a company. As a result, they are able to gain insights into in-demand skills, network, and explore varied career options.
On the other hand, community projects are experiential activities that help students learn skills and make a positive impact on society. Institutes can work with non-profit organisations to conduct tree-planting initiatives, health awareness programs, water conservation programs, etc. Students can participate in such community projects, helping to foster social responsibility and enhance their learning experience.
Tech-Enabled Experiential Activities
Educators can leverage technological solutions like Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) to create an immersive learning environment. For instance, it might not be possible for institutes to facilitate field trips; that is when teachers can do virtual field trips through VR.
Likewise, they can create simulations with the help of AR and VR to demonstrate medical procedures and machinations of a complex structure or process. Additionally, students can take part in such activities, allowing them to practice and learn within a safe environment.
How Learning Management Software Reshapes Education?
How Does Experiential Learning Help Students?
Experiential learning emphasises the active participation of students, improving engagement, developing skills, and a host of other advantages such as:
- Enhances Retention & Understanding: Applying knowledge in real-life situations helps students retain information and gain a deeper understanding of concepts.
- Develops Critical Thinking & Problem-Solving: Students analyze situations, assess different perspectives, and improve logical reasoning skills.
- Encourages Collaboration & Communication: Group projects, internships, and fieldwork help students work effectively in teams and express their opinions confidently.
- Bridges Theory & Practical Application: Moves beyond theoretical knowledge cramming, connecting concepts to real-world applications.
- Builds Professional & Leadership Skills: Internships and community projects foster essential skills like time management and leadership, preparing students for professional environments.
Conclusion,
Experiential learning is a unique teaching and learning methodology through which students can engage in direct experiences. Activities such as fieldwork, internships, research work, etc., improve students’ critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and adaptability. Institutes and educators must collaborate to ensure proper planning and implementation of experiential learning activities.
The Quickest, Easiest, and Most Trustworthy Educational ERP System to Meet Your Institution's Needs'
Mobile: 08448010216
Email: janki.somani@iitms.co.in











_v2.jpg)



-widgets.jpg)